Welcome to JCA | The Importance of Connected Vehicle Data for Smart Cities
We’re now at the point where we have more connected devices than people on Earth. Soon, there will be more sensors in the world than humans. With so many devices exchanging data, it’s not just an issue of our privacy – it’s also an issue of how to manage all of this data to keep our smart cities working well.
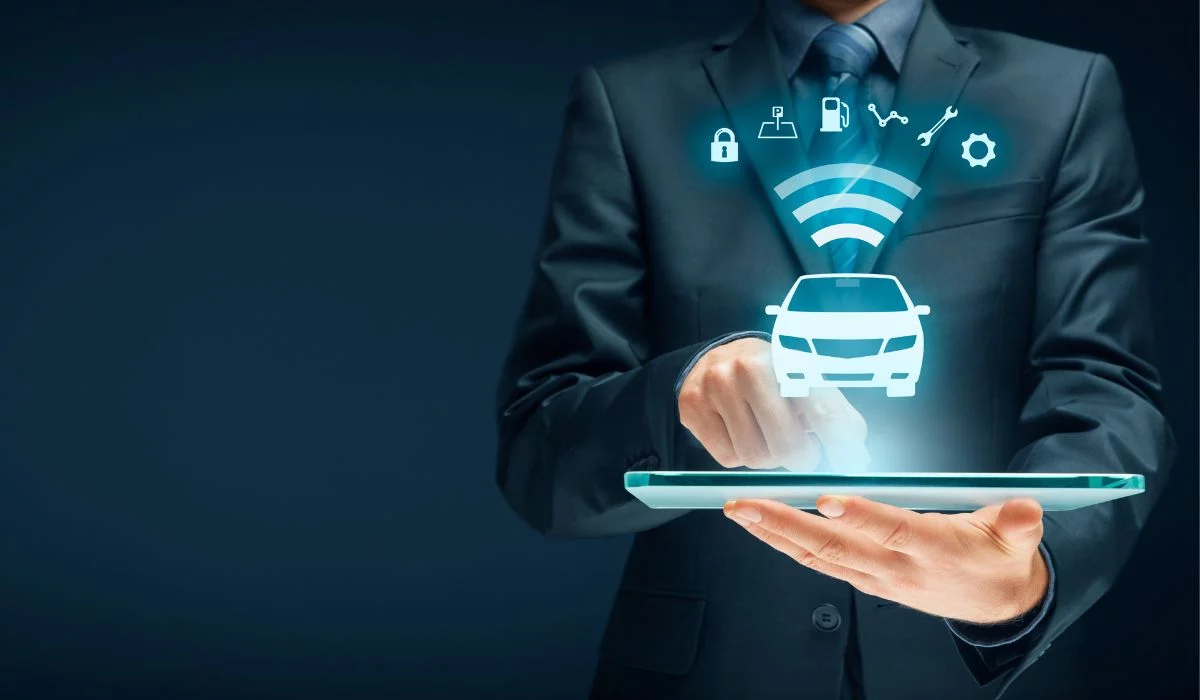
When a city has a network of connected cars, the data these vehicles generate can be leveraged to improve services, reduce congestion and help people get where they’re going.
Connected vehicles are poised to become an integral component of the Smart Cities of the future. As these “smart” transportation networks increase in complexity, there is a critical need for data on traffic patterns, infrastructure status, and congestion reports. This article looks at how connected vehicle data can help make cities smarter, more sustainable, and safer.
Connected Vehicles
In recent years, there has been a growing trend of cities around the world becoming “smart.” By integrating various cutting-edge technologies, smart cities are able to optimize various urban functions and improve the quality of life for citizens. One important element of smart city initiatives is connected vehicles.
Connected vehicles are equipped with sensors and other technology that allows them to communicate with each other and with infrastructures such as traffic lights and road signs. This real-time data exchange enables a number of benefits such as improved traffic flow, reduced accidents, and better management of scarce resources such as parking spots.
For smart city planners, connected vehicle data is a valuable resource that can be used to gain insights into patterns of human behavior and movement. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about urban planning and design. For example, if data shows that a particular intersection is consistently congested at certain times of day, measures can be taken to alleviate the problem such as changing the timing of traffic lights or adding more turning lanes.
Overall, connected vehicle data is playing an increasingly important role in the development of smart cities. By leveraging this data, cities can become more efficient, sustainable, and livable for all residents.
How Connected Vehicle Data Benefits Smart Cities
There are a number of ways that connected vehicle data can benefit smart cities. For one, this data can help city planners to manage traffic flow more effectively. By understanding patterns of vehicle movement, city planners can make better decisions about where to allocate resources and how to design roads. Additionally, this data can be used to improve public safety. For example, if there is a high concentration of connected vehicles in an area, that data can be used to deploy emergency services more efficiently.
Another way that connected vehicle data benefits smart cities is by helping to reduce pollution and save energy. This data can be used to identify areas with a high concentration of vehicle emissions, and then city planners can take steps to mitigate those emissions. Additionally, by understanding patterns of vehicle usage, city planners can develop policies to encourage the use of public transportation and car-sharing, which can lead to reduced traffic congestion and fewer vehicles on the road overall.
How Do Connected Vehicles Work?
In order to function, connected vehicles rely on three key technologies: Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC), cellular networks, and GPS.
DSRC is a two-way wireless communication technology that allows vehicles to exchange safety and operational data with each other, as well as with roadside infrastructure. DSRC-equipped vehicles are equipped with a transceiver, which picks up signals from other DSRC-equipped vehicles and infrastructure within approximately 1000 meters.
Cellular networks are used by some connected vehicle applications to supplement DSRC coverage or provide an alternative communications path. While DSRC offers a direct connection between vehicles and infrastructure, cellular networks provide the added benefit of nationwide coverage. However, cellular networks are subject to potential congestion and data latency issues.
GPS is used by connected vehicle applications to determine the location of participating vehicles. This information is then used to support a variety of safety and operational applications, such as routing advisories, emergency response notifications, and traffic signal timing adjustments.
Why Have Connected Vehicles?
There are many reasons why cities should invest in connected vehicle data systems. These systems improve a city’s efficiency by optimizing the flow of traffic, reducing emissions, and enabling a more coordinated response to emergencies. In addition, these systems can help generate new revenue streams for cities by providing data that can be used for marketing or research purposes.
Most importantly, however, connected vehicle data systems provide cities with invaluable information about their infrastructure and how it is being used. This information can be used to make informed decisions about investments in new or upgraded infrastructure, which can ultimately lead to a more efficient and effective city overall.
Privacy Concerns with Connected Vehicle Data
With the ever-growing popularity of connected and autonomous vehicles, there has been an increase in concern over how these vehicles collect and store data. While the benefits of having a network of connected vehicles are vast, many people are worried about their privacy being invaded by companies collecting this data.
There are a few key ways that companies can collect data from connected vehicles. The first is through sensors that are built into the vehicle itself. These sensors can track everything from the car’s speed and location to the driver’s heart rate and breathing patterns. This data is then transmitted to the cloud, where it can be accessed by the company or sold to third parties.
Another way companies can collect data from connected vehicles is through in-vehicle infotainment systems. These systems allow drivers to connect their smartphones or other devices to the car in order to access music, navigation, and other services. However, this also means that these devices are transmitting data back to the car’s infotainment system, which can then be passed on to the company.
Finally, many connected and autonomous vehicles come with cameras that are used for things like driver assistance and safety features. However, these cameras can also be used to collect personal data about drivers and passengers. For example, some cameras can recognize faces and even read lips, meaning that they could be used to gather sensitive information such as conversations or financial transactions.
All of this data that is collected by companies through connected vehicles can be incredibly valuable. However, it also raises a number of privacy concerns. For example, it is not always clear how this data will be used or who will have access to it. Additionally, there is a risk that this data could be hacked or leaked, exposing people’s personal information to the public.
As the connected and autonomous vehicle industry continues to grow, it is essential to ensure that privacy concerns are addressed. Otherwise, people may be reluctant to use these technologies, which could limit their potential benefits.
Also Check: Top Swift App Development Companies
Challenges Currently Facing Connected Vehicle Data
To approximate this type of data, more people are now using traffic cameras or in-road sensors. A growing number of cities are also making use of public mobile data from personal devices.
Why aren’t more cities using connected vehicle data if it’s so valuable? There are several significant barriers to full adoption and reliance on CVD.
Coverage that is dependable
More vehicles are being produced, but cities still require CVD to be more widespread in order to rely on the data. This could be a non-issue within the next decade. Furthermore, improved coverage from 5G connections will allow cities to gather and extract data more reliably and efficiently.
Various rules and regulations
CVD regulations are still in their early stages, and cities may be hesitant to risk non-compliance. A federal mandate would aid in resolving the issue. Still, when it comes to privacy, states may need to follow California’s lead and take charge without relying on federal guidelines.
Cybersecurity issues
Data collection exposes cities to potential cybersecurity threats. Smart cities, on the other hand, will recognize that data security is critical to the success of data-driven initiatives like these. More cities are responding to cybersecurity threats as a top priority, but being proactive protects everyone.
Citizen confidence
Trust in this new technology has been debated for years (even RTInsights talked about its importance back in 2017). We’ve arrived at a critical juncture. Citizens are divided on the collection of data and the involvement of the government. They want easier access to services and better overall city experiences. If governments can take a transparent approach to collecting and leveraging data like CVD, it will go a long way toward restoring citizen trust.
Also Check: Top Mobile App Design Companies
Connected Vehicle Data and Cloud Computing
The internet of things (IoT) is connecting an ever-growing number of devices and machines to the internet—and to each other. This interconnectivity is transforming how we live, work, and play. It’s also creating new opportunities for cities to become “smart” by using data to improve efficiency, optimize resources, and enhance the quality of life.
One key area where IoT is having a major impact is transportation. In particular, the connected vehicle is becoming an increasingly important part of the smart city landscape. Connected vehicles are equipped with sensors and other technology that enable them to communicate with each other and with infrastructures like traffic lights and road signs. This real-time data exchange has the potential to make our roads safer, reduce congestion, and lower emissions.
To realize these benefits, cities need to be able to collect and analyze large amounts of connected vehicle data. That’s where cloud computing comes in. Cloud-based solutions provide the scalability and flexibility needed to store, process, and visualize data from hundreds or even thousands of connected vehicles. They also offer the computational power required to run advanced analytics that can uncover valuable insights about city traffic patterns, driver behavior, and more.
As more cities embrace connected vehicles, it’s clear that cloud computing will play a vital role in helping them become smarter and more livable places to live.
Also Check: Top SaaS Application Development Companies
Conclusion
CVD must develop into a single data source that can be integrated with data from the current infrastructure. It must also provide consistent, all-encompassing coverage. This offers a system of checks and balances and guarantees the highest level of decision-making for all actions based on this data. As vehicles and infrastructure become more connected, this could be a key factor in bringing cities into the digital age.
If you don’t see what you’re looking for here, reach out to us at [email protected].
Recommended Reading









Leave a Reply