Information Technology (IT) in Supply Chain Management (SCM) represents a pivotal aspect of the modern business landscape. IT, in this context, refers to the systems and software tools that companies use to manage and coordinate all the activities involved in sourcing, procuring, converting, and delivering goods and services. The importance of IT in suply chain management cannot be overstated – it’s like the nervous system of a complex organism, ensuring smooth communication and coordination among various functions and components.
In the fast-paced world of global commerce, businesses need IT to track and manage their supply chains effectively. Supply chain management, when enhanced by IT, allows for more accurate forecasting, increased efficiency, better customer service, and ultimately, improved profitability.
Also read: Importance of Information Technology in Modern Era.
- The Role of Information Technology in Supply Chain Management
- Applications of IT in Supply Chain Management
- 1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
- 2. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
- 3. Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
- 4. Supply Chain Planning (SCP) Software
- 5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
- 6. Business Intelligence and Analytics
- 7. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
- 8. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Benefits of Information Technology in Supply Chain Management
- Challenges of Implementing IT in Supply Chain Management
- Best Practices for Successful Implementation of IT in Supply Chain Management
- Case Studies of Successful IT Implementation in Supply Chain Management
- Future Trends and Emerging Technologies in IT for Supply Chain Management
- Conclusion
The Role of Information Technology in Supply Chain Management
- Enhanced Efficiency: IT streamlines supply chain operations, reducing time and costs.
- Improved Accuracy: IT minimizes human errors in order tracking and inventory management.
- Real-time Tracking: IT enables real-time tracking of goods in transit, increasing reliability.
- Better Demand Forecasting: IT tools analyze market trends for accurate demand prediction.
- Effective Communication: IT facilitates seamless communication between different supply chain stakeholders.
- Risk Management: IT helps identify potential supply chain risks for proactive mitigation.
- Vendor Management: IT simplifies supplier selection, evaluation, and relationship management.
- Sustainability: IT aids in developing environmentally friendly and sustainable supply chains.
- Order Processing: IT automates order processing, increasing speed and efficiency.
- Customer Satisfaction: IT ensures timely delivery and product availability, improving customer satisfaction.
- Data Analysis: IT provides valuable insights into supply chain performance through data analysis.
- Inventory Control: IT systems automate inventory control, preventing overstocking and stockouts.
- Global Operations: IT supports global supply chain operations, overcoming geographical barriers.
- Quality Assurance: IT tools assist in maintaining quality standards across the supply chain.
- Resilience: IT contributes to building a resilient supply chain that can adapt to disruptions.
Applications of IT in Supply Chain Management
Information Technology (IT) has revolutionized Supply Chain Management, creating a more interconnected, transparent, and efficient business environment. IT applications in Supply Chain Management range from comprehensive systems that integrate various business functions, to specialized software for managing warehouses, transportation, and customer relationships. These technological advancements offer myriad benefits, including improved visibility, enhanced collaboration, increased efficiency, and substantial cost savings.
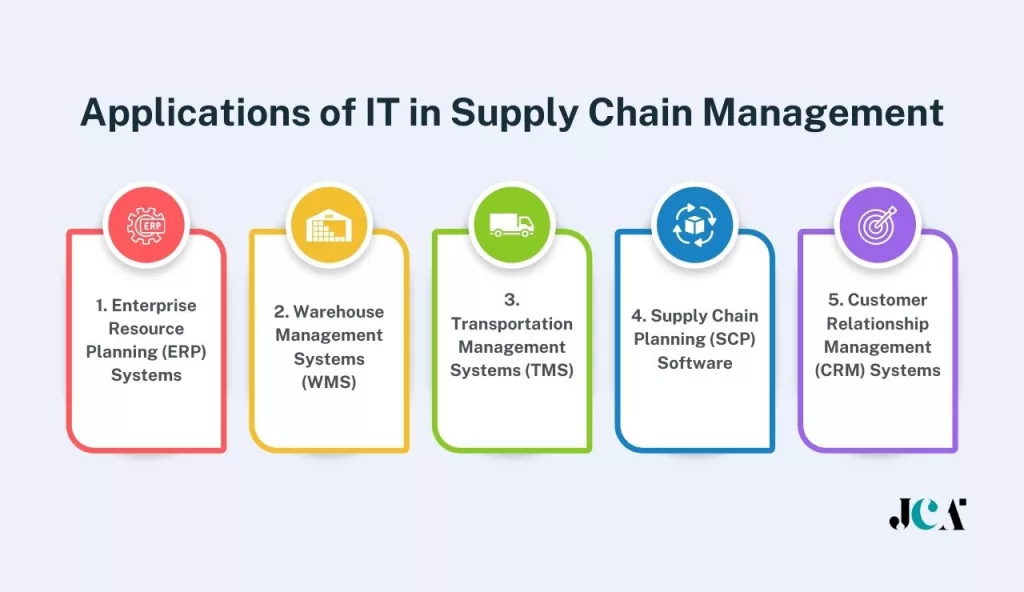
Let’s delve into these applications and explore how they are shaping the future of Supply Chain Management.
1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business functions into one unified platform. This integration streamlines processes, improves data flow, and enhances communication among departments. According to a study by Statista, the global ERP software market is expected to reach $40.5 billion by 2025. ERP systems can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, production schedules, and customer orders, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their supply chains. By automating manual tasks, ERP systems also help reduce human error and improve overall efficiency.
2. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are crucial for controlling the movement, storage, and accounting of materials and goods within a warehouse. These systems offer advanced features such as barcode scanning, real-time inventory tracking, and pick-and-pack processes, ensuring that the right products are shipped to the right customers at the right time. Warehouse Management Software can significantly reduce labor costs, improve space utilization, and increase inventory accuracy. The global warehouse management systems market size is anticipated to reach USD 11.08 billion by 2030, advancing at a CAGR of 16.1% from 2022 to 2030.
3. Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) are software applications that help plan, execute, and optimize the shipments of goods. TMS enables businesses to select the most efficient transportation routes, track shipments in real-time, and manage carrier contracts. TMS can also provide valuable insights into transportation costs and performance, helping companies identify areas for improvement. The global transportation management systems market size was valued at USD 10.45 billion in 2022 and is expected to register a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.8% from 2023 to 2030.
4. Supply Chain Planning (SCP) Software
Supply Chain Planning (SCP) software assists in the planning and execution of supply chain activities, ensuring effective management of demand and supply. SCP tools enable businesses to create accurate demand forecasts, optimize production schedules, and allocate resources efficiently. By providing a holistic view of the supply chain, SCP software helps companies identify potential bottlenecks, minimize risks, and improve overall performance. Market research firm Gartner predicts that the global SCP market will grow at a CAGR of 7.1% through 2022.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential for managing a company’s interaction with current and potential customers. CRM software helps businesses better understand their customers’ needs, preferences, and purchasing habits, leading to improved customer service and enhanced customer retention. CRM systems can also streamline communication with suppliers and other partners, fostering better collaboration across the supply chain. The global CRM software market is expected to reach $58.04 billion by 2023, according to Market Research Future.
6. Business Intelligence and Analytics
Business Intelligence and Analytics tools are indispensable for data analysis, providing insightful information for decision-making processes. These tools enable companies to identify trends, uncover hidden patterns, and detect anomalies in their supply chain data. By harnessing the power of analytics, businesses can make more informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and reduce costs. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global Business Intelligence Market Size is expected to reach USD 54.27 billion in 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.1% between 2023 and 2030.
7. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects, offering real-time tracking capabilities. RFID technology can significantly improve supply chain visibility, inventory management, and asset tracking. With the ability to track individual items throughout the supply chain, businesses can reduce the risk of loss, theft, or counterfeiting.
8. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices — from industrial machines to consumer products — that collect and exchange data. In supply chain management, IoT devices can monitor inventory levels, track goods in transit, and even predict maintenance needs for machinery. By providing real-time data and insights, IoT can help companies manage their supply chains more efficiently and responsively. Research by MarketsandMarkets suggests that the IoT in the manufacturing market is expected to grow from USD 33.2 billion in 2020 to USD 53.8 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 10.1%. This growth indicates the increasing adoption of IoT in supply chain management and the broader manufacturing sector.
Benefits of Information Technology in Supply Chain Management
Information Technology plays a transformative role in supply chain management, offering a multitude of benefits that empower businesses to operate more effectively and strategically. Here are some of the key benefits that IT brings to the table in supply chain management:
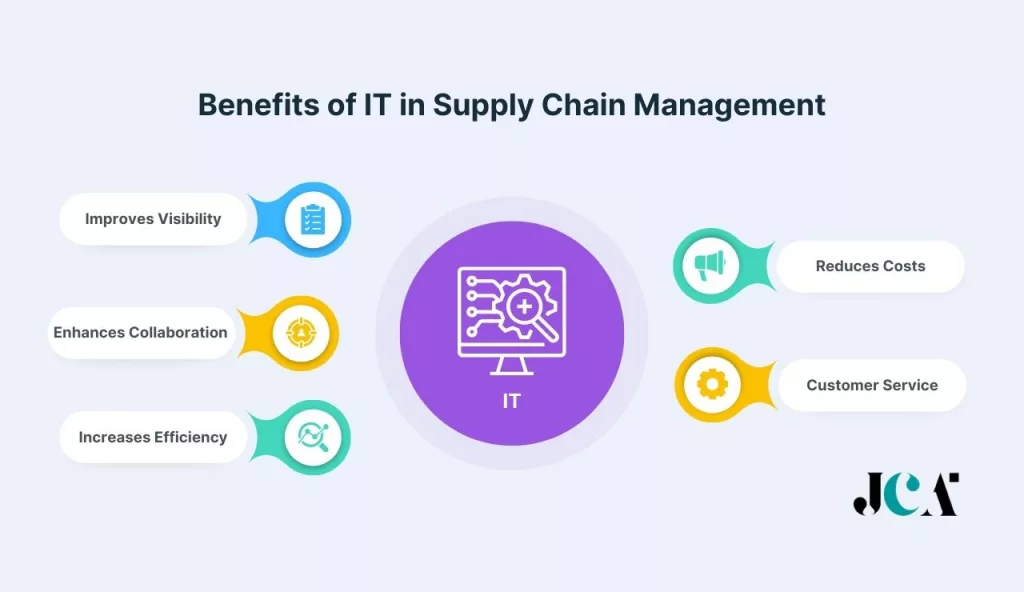
1. Improves Visibility and Transparency
One of the most significant benefits of IT in supply chain management is the improved visibility and transparency it provides. By leveraging technologies like IoT, RFID, and cloud-based software, businesses can gain real-time insights into their supply chains. They can track products from the production floor to the customer’s door, identify potential bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. According to a study by Accenture, 84% of supply chain executives said that the lack of visibility is their biggest challenge. With the help of IT, businesses can overcome this challenge and ensure a smooth, transparent supply chain.
2. Enhances Collaboration and Communication
IT also plays a crucial role in enhancing collaboration and communication among various stakeholders in the supply chain. With tools like ERP and CRM systems, businesses can facilitate information flow, streamline processes, and improve coordination among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. A survey by SCM World found that 79% of companies with high-performing supply chains achieve above-average revenue growth. Enhanced collaboration and communication, driven by IT, are key to achieving such high performance.
3. Increases Efficiency and Productivity
IT applications can significantly increase efficiency and productivity in supply chain manaement. For instance, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) can optimize warehouse space and automate manual tasks, reducing errors and saving time. Similarly, Transportation Management Systems (TMS) can plan the most efficient routes, reducing fuel costs and delivery times. According to Gartner, businesses that have implemented TMS can reduce their freight costs by 5-25%.
4. Reduces Costs and Improved Profitability
By improving efficiency, visibility, and collaboration, IT can ultimately help businesses reduce costs and improve profitability. For instance, better visibility can prevent overstocking or understocking, reducing inventory costs. Likewise, improved efficiency can lower operational costs. According to a Capgemini study, businesses that have digitally transformed their supply chains have achieved a reduction in procurement costs by 20%, inventory costs by 50%, and supply chain costs by 11%.
5. Improves Customer Service and Satisfaction
Last but not least, IT can greatly enhance customer service and satisfaction. CRM systems can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, helping businesses tailor their services and products to meet customer needs. Moreover, improved visibility means customers can track their orders in real-time, enhancing their overall experience. A report by Aberdeen Group found that businesses with integrated CRM systems see a 12.5% increase in customer satisfaction. Thus, IT not only benefits businesses but also creates a better experience for their customers.
Challenges of Implementing IT in Supply Chain Management
While IT offers a multitude of benefits to supply chain management, its implementation is not without challenges. These obstacles can range from technical issues to human-centric concerns. Let’s explore some of the common challenges that businesses may face when implementing IT in their supply chain management:
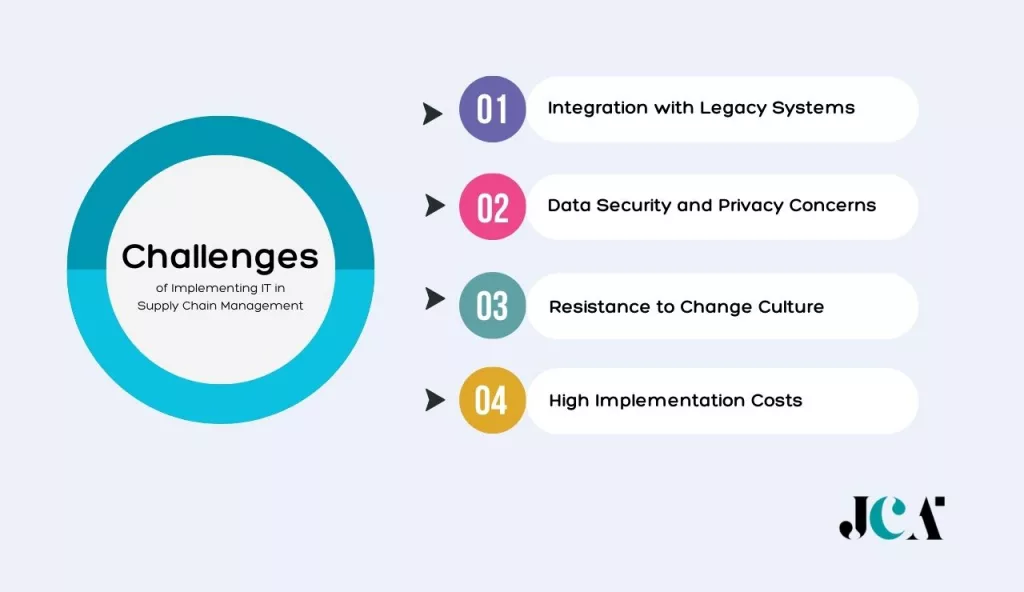
Integration with Legacy Systems
One of the primary challenges is the integration with legacy systems. Legacy systems are older applications or technologies that a company has been using for a long time. These systems may not be compatible with new IT solutions, making integration difficult. Moreover, they often contain critical data and processes that businesses cannot afford to lose or disrupt. Hence, businesses need to plan and execute the integration process carefully to ensure a smooth transition.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
With the increasing use of IT, data security and privacy concerns have become more significant. Businesses need to ensure that their IT systems are secure and that they comply with all relevant data protection regulations. Any breach could lead to severe financial and reputational damage. A study by IBM revealed that the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million. Thus, businesses must invest in robust security measures and practices to protect their data.
Resistance to Change and Organizational Culture
Resistance to change and organizational culture can also pose significant challenges. Implementing new IT solutions often requires changes in business processes and work habits. Employees may resist these changes due to fear of the unknown, lack of understanding, or perceived threats to their roles. Therefore, businesses need to manage change effectively, involving employees in the process, and communicating the benefits of the new IT systems.
High Implementation Costs and Limited Resources
The high implementation costs and limited resources can be a barrier, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. Implementing IT solutions requires substantial financial investment, skilled personnel, and time. Moreover, businesses may need to spend additional resources on training employees and maintaining the IT systems. Therefore, businesses need to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before deciding to implement new IT solutions.
Difficulty Adjusting to New Processes and Tools
Employees might have difficulty adjusting to new processes and tools. This could lead to a decrease in productivity and morale, at least in the short term. Businesses need to provide adequate support and training to help employees adapt to the new IT systems.
Inadequate Practice and Training Prior to Introduction
Inadequate practice and training prior to the introduction of the new IT systems can lead to implementation failures. Employees need to understand how to use the new systems effectively and how they can benefit their work. Thus, businesses should provide comprehensive training and allow sufficient practice time before fully implementing the new systems.
Communication Issues
Lastly, communication issues both within and outside the organization can hinder the successful implementation of IT. For instance, businesses need to communicate clearly with their IT vendors to ensure that the new systems meet their needs. Similarly, they need to communicate with their customers to manage expectations and address any concerns or issues promptly.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation of IT in Supply Chain Management
Successfully implementing IT in supply chain management can be a complex and challenging process. However, by following some best practices, businesses can navigate this process more effectively and maximize the benefits of their new IT systems. Here are some of the key practices to consider during the implementation process:
Define Clear Objectives and Goals
Before embarking on the implementation process, businesses should define clear objectives and goals. What problems are they trying to solve? What benefits do they expect from the new IT systems? By answering these questions, businesses can establish a clear direction for the implementation process and measure their success more accurately.
Conduct a Comprehensive Needs Assessment
Next, businesses should conduct a comprehensive needs assessment. This involves examining their current supply chain processes, identifying gaps and inefficiencies, and understanding their specific needs. This assessment will help them choose the right IT solutions that meet their unique requirements.
Select the Right Technology and Vendor
Selecting the right technology and vendor is a critical step. Businesses should consider factors such as the technology’s features, compatibility with existing systems, cost, vendor’s reputation, and support services. They can also seek recommendations from industry peers or consult with IT experts to make an informed decision.
Develop a Robust Implementation Plan
A robust implementation plan can guide businesses through the implementation process and ensure that all critical aspects are considered. The plan should include timelines, responsibilities, risk management strategies, and contingency plans. By having a well-developed plan, businesses can manage the implementation process more effectively and mitigate potential risks.
Ensure User Adoption and Training
To maximize the benefits of the new IT systems, businesses need to ensure user adoption and provide adequate training. They should involve users early in the process, address their concerns, and provide comprehensive training. This will help users understand the benefits of the new systems, how to use them effectively, and how they will impact their roles.
Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Finally, businesses should continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of the new IT systems. They can use key performance indicators (KPIs) related to their objectives and goals to measure success. By monitoring and evaluating performance, businesses can identify any issues early, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the new IT systems are delivering the expected benefits.
Case Studies of Successful IT Implementation in Supply Chain Management
The impact of IT on supply chain management can be better understood through real-world examples. Here are four major corporations that have successfully implemented IT in their supply chain management:
Walmart
Walmart is a prime example of successful IT implementation in supply chain management. Its sophisticated IT systems provide real-time inventory data and automated replenishment processes. The company has also implemented RFID technology to track products and reduce theft. These IT implementations have made Walmart’s supply chain one of the most efficient in the world, enabling it to offer low prices to its customers.
Amazon
Amazon has revolutionized the e-commerce industry with its innovative use of IT in supply chain management. The company uses advanced algorithms and machine learning to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and enable fast delivery. It also uses robotics and automation in its warehouses to increase efficiency. As a result, Amazon has become synonymous with convenience and fast delivery.
Procter & Gamble
Procter & Gamble (P&G) has leveraged IT to create a demand-driven supply chain. The company uses real-time sales data to forecast demand and adjust production accordingly. It has also implemented a collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment (CPFR) system to improve collaboration with retailers. These IT implementations have helped P&G reduce stockouts and overstocks, improving customer satisfaction.
Toyota
Toyota is known for its lean manufacturing philosophy, and IT plays a crucial role in it. The company uses IT systems to synchronize production with demand, reduce waste, and improve quality. For instance, it uses a Just-In-Time (JIT) system to ensure that parts are delivered to the production line exactly when they are needed. This has helped Toyota achieve high efficiency and quality in its production.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies in IT for Supply Chain Management
As we look towards the future, several emerging technologies promise to further transform supply chain management:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize supply chain management. They can analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling more accurate demand forecasting, dynamic pricing, and predictive maintenance.
Blockchain
Blockchain offers a secure and transparent way to record transactions, making it ideal for supply chain management. It can enhance traceability, reduce fraud, and improve contract enforcement.
Augmented and Virtual Reality
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) can enhance various aspects of supply chain management, from warehouse management to employee training and customer service.
Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Autonomous vehicles and drones can automate transportation and delivery processes, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
Cloud computing and edge computing offer flexible and efficient ways to store and process data, making supply chain processes more responsive and adaptable.
Conclusion
Information Technology plays an indispensable role in modern Supply Chain Management. From improving visibility and efficiency to enhancing collaboration and customer service, IT offers a multitude of benefits. While implementing IT can be challenging, the potential rewards make it a worthwhile investment. As we look towards the future, emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and autonomous vehicles promise to further transform supply chain management. Therefore, businesses need to stay abreast of these trends and continue to leverage IT to enhance their supply chain management.









Leave a Reply