The manufacturing industry is on the brink of a revolution with the Internet of Things (IoT). Traditional factories, with their large assembly lines and hum of industrial machines, are evolving into more intelligent, connected, and efficient production facilities.
At the heart of this change is IoT — a network of machines, devices, sensors, and humans that are connected, communicating, and collaborating with each other in real-time. The Internet of Things provides visibility and control over every part of the manufacturing process.
The IoT plays an essential role in today’s manufacturing processes. With IoT our traditional, linear manufacturing landscapes are being transformed into dynamic and intelligent ecosystems faster. Ecosystems that can self-adapt, self-learn, and self-optimize, often with little to no human intervention.
This is a shift that is already producing sizable improvements in productivity and operational efficiency and at the same time opening new channels for innovation and customization that can meet the ever-changing demands of the consumer market at an accelerated pace.
In this blog post, we will examine exactly what IoT in manufacturing means — covering its past, the key technologies involved, and the many ways it’s benefiting the industry.
- Evolution of IoT in Manufacturing
- IoT Market Size in the Manufacturing Industry
- Key Technologies and Their Applications in IoT in Manufacturing
- What are the Top Benefits of IoT in the Manufacturing Industry?
- What are the Examples of IoT Success in Manufacturing?
- Challenges and Solutions in IoT Adoption in Manufacturing
- Future Trends and Predictions in IoT for Manufacturing
- Final Words
Evolution of IoT in Manufacturing
The journey of IoT in manufacturing is a tale of technological evolution. Its origins go back decades to the dawn of early automation systems in the 1970s. These early systems were groundbreaking for their time — but they were also limited in what they could do. They couldn’t talk to one another. They couldn’t adapt to changes in conditions.
Fast forward to the 1990s and the internet began to reshape our world. Yet it was still in its infancy in its penetration into manufacturing.
Fast forward into the 21st century, and now IoT has started to take form. Manufacturers began to imagine world of internet-connected devices — machines that could communicate and eliminate downtime; that could predict failures and order their own replacement parts ahead of time; and could adjust production without human hands. This vision was the birthplace of what we today call IoT in manufacturing.
And now we stand at an incredible juncture of time — IoT as reality. Factories from around the world have more sensors, robots, and smart devices than ever. And those are devices that collect and analyze data in real-time. Those are machines making decisions that used to be in the hands of the human on the factory floor.
It’s a monumental shift, because it’s not just automation — it’s smart automation. Machines that predict when they need maintenance, that adjust to unknown changes in production demand, or even manage the inventory themselves.
Also read: Top 15 IoT Cloud Platforms that are shining
IoT Market Size in the Manufacturing Industry
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) helps making traditional factories into smart spaces.
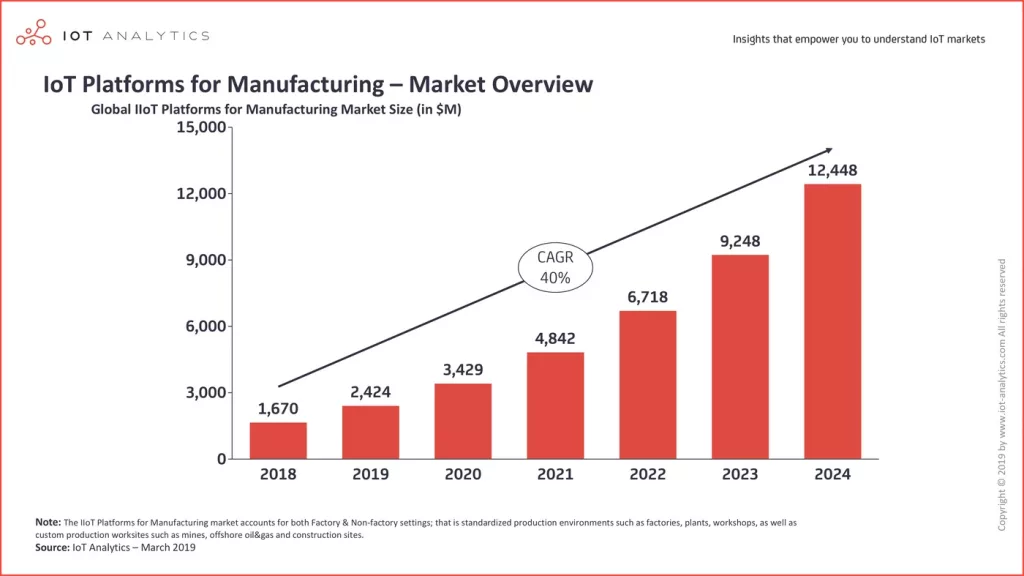
- The global Internet of Things (IoT) market is forecast to be worth around 336 billion U.S. dollars in 2025, and rise to more than 621 billion U.S. dollars in 2030, tripling its revenue in ten years. Not only this, but the number of IoT connected devices worldwide is forecast to triple during this span of time.
- According to the latest predictions from technology experts at IDC, by 2025, we’re expected to see 55.7 billion devices connected through the Internet of Things (IoT), which will produce nearly 80 zettabytes of data. To put this into perspective, as of 2023, Ericsson’s Mobility Report showed that there were around 15.7 billion IoT connections.
- In the US, about 35% of manufacturing companies are already using data from smart sensors to improve their operations.
- A report by PwC shows that 90% of manufacturers believe going digital with their production processes will bring more benefits than risks in the long run.
- Experts predict that industries like discrete manufacturing, transportation & logistics, and utilities will each spend around $40 billion on IoT technologies and services.
- According to Accenture, 46% of American companies view IoT as a chance to boost employee productivity.
- Furthermore, 58% of manufacturers consider IoT essential for digitally transforming industrial operations, although the high cost of investment is seen as the main hurdle to adopting IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) more quickly.
Also read: How to Create An IoT App – Time, Cost, and Resources You Need
Key Technologies and Their Applications in IoT in Manufacturing
IoT in manufacturing is powered by several key technologies. Each plays a crucial role in transforming traditional factories into smart manufacturing hubs. Let’s explore these technologies and see how they apply in the manufacturing sector.
Sensors and Devices: The Eyes and Ears
Sensors and devices are the frontline soldiers of IoT. They gather data from machines and the environment. Think of them as the eyes and ears of a factory. They monitor everything from temperature to machine performance. This real-time data is gold. It helps manufacturers spot issues before they escalate, saving time and money.
Connectivity Solutions: The Nervous System
Connectivity solutions are the backbone, acting as the nervous system of IoT. They ensure data flows smoothly from sensors to decision-makers. Without reliable connectivity, IoT is like a brain without a spinal cord. Technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G keep this flow uninterrupted. They enable devices to communicate, ensuring operations run smoothly.
Data Analytics and AI: The Brain
Data analytics and AI form the brain of IoT operations. They take data and turn it into insights. Imagine having the power to predict machine failures or optimize production schedules. That’s what analytics and AI do. They analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and suggest actions. This intelligence is key to making informed decisions quickly.
Cloud Computing: The Infinite Library
Cloud computing offers endless storage and powerful computing capabilities. It’s like an infinite library, holding and processing data from across the factory. The cloud makes data accessible anywhere, anytime. It supports analytics and AI, enabling them to work on massive datasets without onsite hardware limitations.
The combination of these technologies revolutionizes manufacturing. Sensors ensure precise monitoring. Connectivity keeps data flowing. Analytics and AI provide actionable insights. The cloud offers the infrastructure to support it all. Together, they create a smart manufacturing environment where efficiency and innovation thrive.
You might like checking the Fastest Growing IoT Companies.
What are the Top Benefits of IoT in the Manufacturing Industry?
The integration of IoT technologies in manufacturing brings a multitude of benefits. These advantages not only enhance production efficiency but also improve product quality, worker safety, and supply chain management. Let’s delve into these benefits, showcasing how IoT is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape.
1. Increases Operational Efficiency
- Real-Time Monitoring and Control: IoT enables real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes. This immediacy allows for swift adjustments, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity. For instance, if a machine starts operating outside its optimal parameters, IoT systems can alert managers or even autonomously adjust the machine’s settings to prevent disruptions.
- Automation and Process Optimization: Through automation, IoT reduces the need for manual intervention, streamlining operations. Process optimization further ensures that manufacturing runs smoothly and efficiently, cutting costs and boosting output.
2. Enhances Product Quality
- Consistent Monitoring: Constant monitoring means that any deviation from quality standards is immediately detected and addressed. This ensures that products meet strict quality criteria consistently.
- Predictive Maintenance: By predicting when equipment might fail or require maintenance, IoT helps avoid the production of defective goods. Keeping machinery in optimal condition is key to maintaining high-quality production standards.
3. Improves Worker Safety
- Environment Monitoring: IoT devices can monitor conditions that may affect worker safety, such as toxic gas levels, temperature, or machinery malfunctions. Immediate alerts can be sent out to prevent accidents.
- Wearable Safety Devices: Workers equipped with IoT-enabled wearables can be monitored for signs of fatigue, overheating, or other health concerns, ensuring that help can be provided promptly when needed.
4. Supply Chain Optimization
- Real-Time Tracking: IoT enables the real-time tracking of materials and products throughout the supply chain. This visibility allows for more accurate inventory management and reduces the likelihood of shortages or overstocking.
- Demand Forecasting: By analyzing data collected from various sources, IoT can help predict future demand more accurately, enabling manufacturers to adjust their production schedules accordingly, ensuring they meet demand without excessive inventory buildup.
Also look at the top Supply Chain Companies
The benefits of IoT in manufacturing are clear and transformative. Increased operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, improved worker safety, and optimized supply chain management are just the beginning. As manufacturers continue to harness the power of IoT, the potential for innovation and growth seems limitless.
What are the Examples of IoT Success in Manufacturing?
Exploring real-world applications of IoT in the manufacturing industry can provide valuable insights into its transformative power. Here are a few case studies that highlight how companies have successfully implemented IoT solutions to overcome challenges, improve processes, and achieve significant outcomes.
Smart Factory Transformation
Company: Tata Automobiles – A leading automotive manufacturer.
Challenge: Tata faced issues with production inefficiencies, high operational costs, and a lack of real-time data to make informed decisions.
Solution: Implementation of a comprehensive IoT platform that integrated sensors, connectivity solutions, and analytics across the production line. This system enabled real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, predictive maintenance, and automated quality control.
Outcome: The company saw a 20% increase in production efficiency, a 15% reduction in operational costs, and a significant improvement in product quality. Real-time data analytics also allowed for more agile decision-making processes.
Enhancing Worker Safety Through IoT
Company: Texmark Chemicals – A multinational chemical processing firm.
Challenge: Worker safety was a significant concern due to the hazardous nature of the chemicals handled and the complex processes involved.
Solution: Deployment of IoT-enabled wearable devices for workers, which monitored health indicators and environmental conditions in real-time. The system also included emergency alerts and automated safety measures in case of hazardous conditions.
Outcome: The implementation led to a 40% reduction in workplace accidents and significantly improved response times to potential safety incidents. Worker satisfaction and compliance with safety protocols also increased.
Supply Chain Optimization
Company: Apple – A global consumer electronics producer.
Challenge: The company struggled with supply chain inefficiencies, including inventory mismatches, delayed shipments, and a lack of visibility into the supply chain.
Solution: The company adopted an IoT-based supply chain management system that provided real-time tracking of materials and products, demand forecasting, and inventory optimization.
Outcome: The solution resulted in a 25% improvement in supply chain efficiency, reduced inventory costs by 30%, and enhanced customer satisfaction due to better on-time delivery rates.
These case studies underscore the potential of IoT to revolutionize manufacturing. By embracing IoT, companies can address a wide range of challenges, from improving operational efficiency and product quality to enhancing worker safety and optimizing the supply chain. The key to success lies in the strategic implementation of IoT technologies tailored to specific needs and challenges.
Also read: Applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) in Education
Challenges and Solutions in IoT Adoption in Manufacturing
While the benefits of IoT in manufacturing are significant, the path to successful implementation can be fraught with challenges. Understanding these obstacles and identifying effective solutions is crucial for manufacturers aiming to leverage IoT technology. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Security Concerns
Security risks are a top concern for manufacturers integrating IoT into their operations. The increased connectivity and data sharing inherent in IoT systems can expose manufacturers to cyber threats.
Solution: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential. This includes regular software updates, secure data encryption, and the adoption of industry-standard security protocols. Conducting regular security audits and training employees on cybersecurity best practices can also fortify defenses against cyber threats.
Challenge 2: Data Privacy
Data privacy becomes a complex issue with IoT, as vast amounts of data are collected and analyzed. Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information is paramount.
Solution: Manufacturers should adopt clear data privacy policies and comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR. Employing data anonymization techniques and secure access controls can help protect privacy while allowing the beneficial use of data.
Challenge 3: Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating IoT solutions with existing manufacturing systems and technologies can be challenging. Compatibility issues and the complexity of existing IT infrastructures can hinder seamless integration.
Solution: A phased approach to integration, starting with pilot projects to test compatibility and gradually expanding, can be effective. Choosing IoT solutions that offer flexibility and compatibility with existing systems, or investing in middleware, can also ease integration.
Challenge 4: Skill Gaps
The lack of skilled personnel familiar with IoT technologies can pose a significant barrier to adoption. The successful implementation of IoT requires a workforce skilled in data analytics, cybersecurity, and IoT device management.
Solution: Investing in training and development programs for existing staff can help bridge this skill gap. Additionally, partnering with IoT solution providers that offer comprehensive support and training can facilitate a smoother transition to IoT-enabled manufacturing.
Moving Forward
Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic approach that includes careful planning, investment in security and privacy measures, a focus on integration and compatibility, and a commitment to workforce development. By addressing these issues head-on, manufacturers can unlock the full potential of IoT to drive innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness in the digital age.
Also read: Future of IoT in Healthcare
Future Trends and Predictions in IoT for Manufacturing
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, the role of IoT is becoming increasingly significant, driving innovation and efficiency to new heights. Let’s explore the emerging trends in IoT within manufacturing and what they could mean for the future of the industry.
Greater Integration of AI and Machine Learning
What’s Happening: AI and machine learning are becoming more deeply integrated with IoT. This fusion is enabling smarter, more adaptive manufacturing processes that can learn and improve over time.
What It Means: Expect production lines that can autonomously adjust to changes in demand, optimize themselves for efficiency without human intervention, and predict maintenance needs to prevent downtime.
Advanced Robotics and Automation
What’s Happening: Robots are becoming more sophisticated and capable of performing complex tasks alongside human workers. IoT is facilitating this shift, allowing robots to communicate with other machines and make decisions based on real-time data.
What It Means: This trend will lead to more flexible and efficient manufacturing floors where robots handle dangerous or repetitive tasks, improving safety and freeing up human workers for more strategic roles.
Also read: The Birth Of The New Manufacturing Industry 4.0 – Automation AI And Robotics
Digital Twins and Simulation
What’s Happening: The use of digital twins, or virtual replicas of physical systems, is on the rise. These digital models can simulate the performance of a manufacturing system under various conditions, informed by real-time IoT data.
What It Means: Manufacturers will be able to predict outcomes more accurately, test changes virtually before implementing them, and optimize processes with a level of precision previously unattainable.
Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility and Collaboration
What’s Happening: IoT is enabling unprecedented levels of visibility and collaboration across the supply chain. Real-time tracking of materials and products ensures that manufacturers can respond quickly to changes and disruptions.
What It Means: This trend will lead to more resilient supply chains, where manufacturers can adapt to shortages, delays, or changes in demand with agility, minimizing disruptions and maintaining steady production flows.
Focus on Sustainability

What’s Happening: There’s a growing emphasis on using IoT to achieve sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes monitoring and reducing energy consumption, optimizing resource use, and minimizing waste.
What It Means: IoT will play a crucial role in making manufacturing more environmentally friendly. By optimizing processes and reducing waste, manufacturers can lower their carbon footprint while also cutting costs.
Looking Ahead
The future of IoT in manufacturing is bright, with technologies that promise to make factories smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable. As these trends continue to unfold, manufacturers who embrace IoT and its advancements will find themselves at the forefront of innovation, ready to meet the challenges of the 21st century.
Also read: The Role of IoT in Industrial Automation
Final Words
The role of IoT in manufacturing is transformative, offering numerous benefits and paving the way for a future where smart, efficient, and sustainable manufacturing is the norm. The industry is on the cusp of a new era, driven by technological advancements that promise to redefine what’s possible on the manufacturing floor.








Leave a Reply